
Manufacturing companies offer a good example of how depreciation can affect book value. These companies have to pay huge amounts of money for their equipment, but the resale value for equipment usually goes down faster than a company is required to depreciate it under accounting rules. Sandra Habiger is a Chartered Professional Accountant with accounting in 2040 a Bachelor’s Degree in Business Administration from the University of Washington. Sandra’s areas of focus include advising real estate agents, brokers, and investors. She supports small businesses in growing to their first six figures and beyond. Alongside her accounting practice, Sandra is a Money and Life Coach for women in business.
Methods to Increase the Book Value Per Share
The market value of a company is based on the current stock market price and how many shares are outstanding. Assume that XYZ Manufacturing has a common equity balance of $10 million and 1 million shares of common stock are outstanding. This means that the BVPS is ($10 million / 1 million shares), or $10 per share. If XYZ can generate higher profits and use those profits to buy assets or reduce liabilities, the firm’s common equity increases. Book value per share relates to shareholders’ equity divided by the number of common shares.
Limitations of BVPS
A price-to-book ratio under 1.0 typically indicates an undervalued stock, although some value investors may set different thresholds such as less than 3.0. Even though book value per share isn’t perfect, it’s still a useful metric to keep in mind when you’re analyzing potential investments. In other words, investors understand the company’s recent performance is underwhelming, but the potential for a long-term turnaround and the rock-bottom price can create a compelling margin of safety. The difference between book value per share and market share price is as follows. The figure of 1.25 indicates that the market has priced shares at a premium to the book value of a share. The ratio may not serve as a valid valuation basis when comparing companies from different sectors and industries because companies in other industries may record their assets differently.
How does BVPS differ from market value per share?
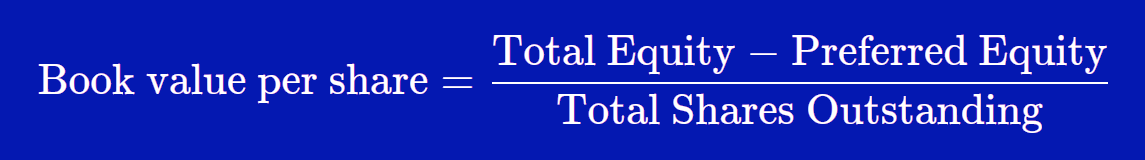
The formula for BVPS involves taking the book value of equity and dividing that figure by the weighted average of shares outstanding. A P/B ratio of 1.0 indicates that the market price of a share of stock is exactly equal to its book value. For value investors, this may signal a good buy since the market price generally carries some premium over book value. There is a difference between outstanding and issued shares, but some companies might refer to outstanding common shares as issued shares in their reports. You should consider here all non-physical assets such as goodwill and intangible assets recorded by the acquisition of another company.
- The book value per share (BVPS) metric helps investors gauge whether a stock price is undervalued by comparing it to the firm’s market value per share.
- Those are two of the main questions we ask while formulating an investment thesis.
- Should the company dissolve, the book value per common share indicates the dollar value remaining for common shareholders after all assets are liquidated and all creditors are paid.
- In theory, book value should include everything down to the pencils and staples used by employees, but for simplicity’s sake, companies generally only include large assets that are easily quantified.
- A company can use a portion of its earnings to buy assets that would increase common equity along with BVPS.
Book value is the value of a company’s assets after netting out its liabilities. It approximates the total value shareholders would receive if the company were liquidated. BVPS is significant for investors because it offers a snapshot of a company’s net asset value per share. By analyzing BVPS, investors can gain insights into a company’s financial health and intrinsic value, aiding in the assessment of whether a stock is over or undervalued. In closing, it’s easy to see why the book value per share is such an important metric. It’s a simple way to compare the value of a company’s net assets to the number of shares that are outstanding.
Why is BVPS important for value investors?
One limitation of book value per share is that, in and of itself, it doesn’t tell you much as an investor. Investors must compare the BVPS to the market price of the stock to begin to analyze how it impacts them. On the other hand, if a company with outdated equipment has consistently put off repairs, those repairs will eat into profits at some future date. This tells you something about book value as well as the character of the company and its management. You won’t get this information from the P/B ratio, but it is one of the main benefits of digging into the book value numbers and is well worth the time.
BVPS relies on the historical costs of assets rather than their current market values. This approach can lead to significant discrepancies between the book value and the actual market value of a company’s assets. Book Value Per Share (BVPS) is a crucial financial metric that indicates the per-share value of a company’s equity available to common shareholders. It helps investors determine if a stock is overvalued or undervalued based on the company’s actual worth. A simple calculation dividing the company’s current stock price by its stated book value per share gives you the P/B ratio. If a P/B ratio is less than one, the shares are selling for less than the value of the company’s assets.
Book Value Per Share solely includes common stockholders’ equity and does not include preferred stockholders’ equity. This is because preferred stockholders are ranked differently than common stockholders in the event the company is liquidated. A company’s stock buybacks decrease the book value and total common share count. Stock repurchases occur at current stock prices, which can result in a significant reduction in a company’s book value per common share. Book value is the value of a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities. The book value per share (BVPS) metric helps investors gauge whether a stock price is undervalued by comparing it to the firm’s market value per share.
